Debt Settlement vs. Debt Management: Which Is Better for You?
About Stefanie
Stefanie began her career as a journalist, reporting on options, futures, and pension funds, and most recently worked as a writer and SEO content strategist at a digital marketing agency. In her free time, she enjoys teaching Pilates and spending time with her daughter and Siberian Husky.
Read full bio
At a Glance
Debt management programs and debt settlement can both help relieve you of your debt. But each has its advantages and disadvantages.
This article will cover:
What is debt settlement?
Debt settlement is a strategy in which you stop making payments to your creditors, typically for a few months or longer. You’ll then request that the creditor take a portion of the amount you owe as full payment, and to forgive the rest, the hope being that the creditor will reason that some payment is better than no payment.
You’ll typically work with a debt settlement company. Monthly payments will be made to the company, and when they feel that you’ve paid a certain percentage of the owed amount, they’ll make the creditor a lump-sum offer. If your offer is accepted, your debt could be forgiven.
Advantages of debt settlement
- Can help you avoid declaring bankruptcy
- Has the potential to drastically reduce the amount you’ll pay
Disadvantages of debt settlement
- The creditor may not necessarily agree to the offer (some businesses refuse to deal with debt settlement companies altogether)
- Could result in your being sued by the creditor
- Collections agencies will most likely try and contact you about your missed payments
- Will severely damage your credit score, and the damage will remain on your score for 7 years
- Your debt will increase due to interest accrued and late charges from your creditors
- Fees for using a debt settlement company have the potential to erase any money being saved
- You could be taxed on the amount forgiven, as it is typically reported to the IRS as income
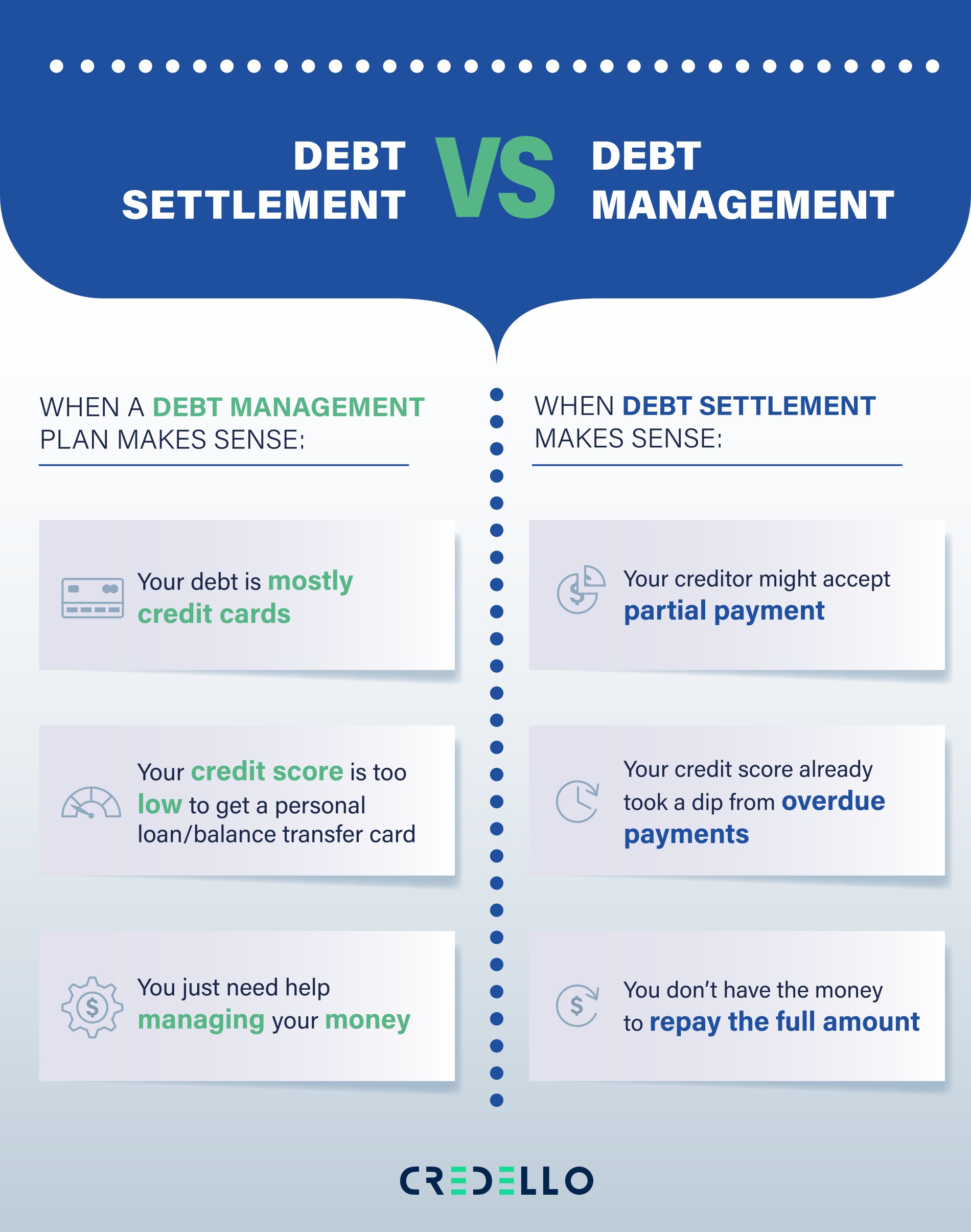
Debt settlement is best if:
- Your credit score is already damaged by an account that’s already overdue or in collections
- You think your creditor may accept a partial payment.
What is debt management?
A debt management plan can help you eliminate credit card debt by consolidating multiple debts into one payment that you’ll pay off monthly. You’ll work with and make your payments to a nonprofit credit counseling agency who will help you set up a 3-5 year repayment strategy. The agency will most likely try to negotiate a lower interest rate with your creditors, as well as lower other charges i.e. late fees.
Advantages of debt management
- You’re still paying off the full principal so your credit score will not suffer as it would with a debt settlement plan
- Because you’re paying your entire debt off, you’ll save on interest
- Once creditors accept the terms of your debt management program, they will stop calling you/sending letters
- Your credit counseling agency will help you structure your repayment schedule, so you’ll have a definitive plan of action
Disadvantages of debt management
- While on the plan, you won’t be able to use credit cards or open a new line of credit
- Your debt won’t be forgiven instantly—it could take up to 5 years to pay it off entirely
Debt management is best if:
- Your credit score is too low to obtain a personal loan or balance transfer card
- Your debt is mostly from credit cards.
Which should you choose?
When deciding whether to go with debt settlement or debt management, you should consider your ability to pay off debt you have.
If you feel like you’re completely out of choices and your debt seems insurmountable, you may want to consider debt settlement. However, given the downsides associated with debt settlement, it should be considered a last resort right before bankruptcy.
If your issue is mainly in money management, and you have the funds to begin paying back your debt, working with a debt management company will be the better choice. It will take commitment and time, but you won’t hurt your credit and you’ll pay off the entire amount owed.