What are the Different Credit Score Ranges?
About Molly
Molly is a finance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She also covers software and environmental issues and is always on the lookout for a good vegan donut.
Read full bio
At a Glance
When taking out a loan or applying for a credit card, your credit score determines so much. Ten points can mean the difference between getting approved and getting turned down. To better understand your credit score, it’s important to know the range of scores and different scoring models.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What are credit score ranges
- How can you check your credit range
- What do the credit score ranges mean for you
- Why are there different credit score ranges
- How lenders use your credit score range
- Why does having a good credit score matter
- How’s the credit score calculated
- What is the highest credit score
- What is the lowest score possible
- Average credit score in the U.S.
- Improving credit score
- How long will It take to get a good credit score
- FAQs
A credit score is a three-digit number that reflects your credit health and ability to repay new debt, such as a loan or credit card. It also helps determine the interest rate you’d pay, how much you’re approved for, and other aspects. Scores typically range from 300 to 850.
These scores are calculated from information about your credit reports (like loan payment history and credit card balances) and provided by the three credit bureaus Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. This means you can have multiple credit scores that may vary slightly since each bureau calculates their scores differently. However, the most well-known scoring model is known as FICO.
High credit scores typically indicate low-risk borrowers, so you’ll have access to more and better credit products at lower interest rates. Low credit scores often represent high-risk borrowers, who would in turn have fewer financing options at higher interest rates.
What are credit score ranges?
When you apply for a credit card or loan, the lender checks your credit score to assess risk. However, there isn’t just one “credit Score.” You actually have many scores across different credit bureaus and credit products. You may see discrepancies based on who reports your score (more on that below).
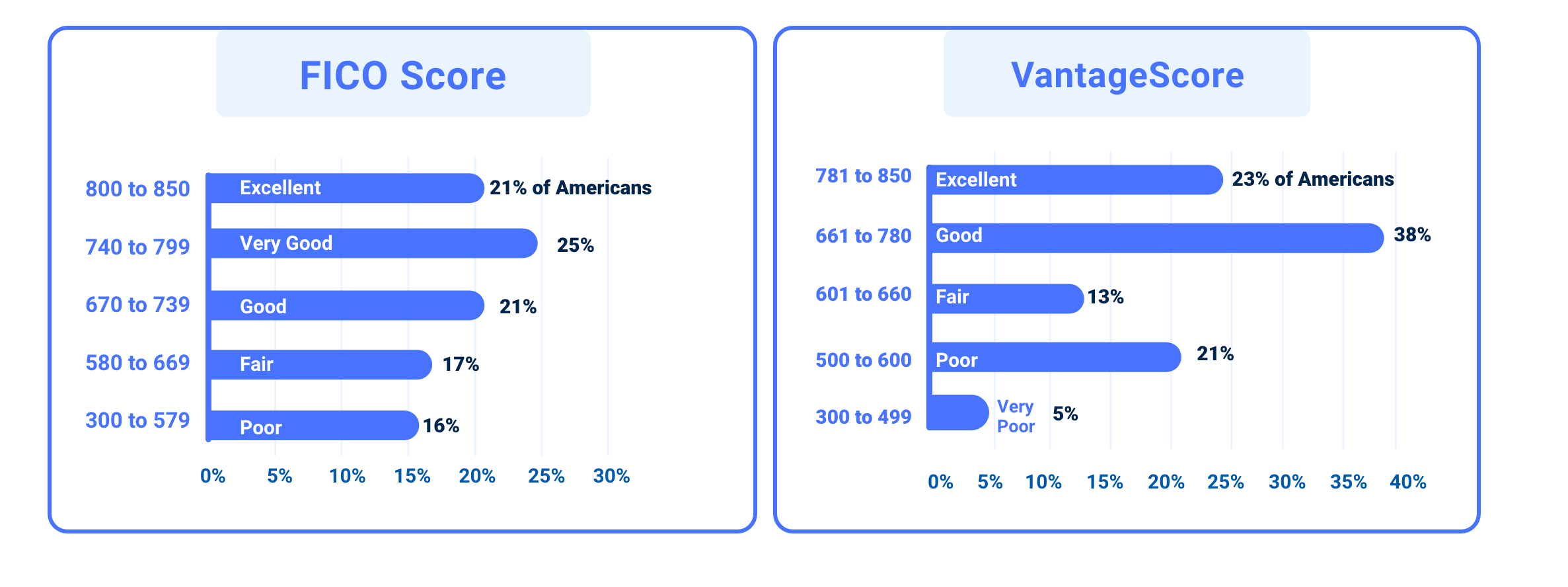
FICO vs VantageScore ranges
Let’s compare the ranges of the most common credit-scoring systems, FICO and VantageScore. They use the same three-digit range, from 300 to 850. The higher your score, the better your credit. For both systems, a good score is around 690 and up.
Source: Experian
How can you check your credit range?
There are several ways you can check your credit range for free, including:
- AnnualCreditReport.com provides one free report per bureau per year.
- MyFico.com can provide your FICO score for free.
- Create a myEquifax account to get six free Equifax credit reports each year.
- Experian offers a free report and FICO score, as well as credit monitoring and other benefits.
- VantageScore partners with a number of institutions to provide your score.
- Some credit cards, financial institutions, banks, and loan statements provide credit scores on your statements.
Related: Does Checking Your Credit Score Lower It?
It’s crucial to keep an eye on your credit score, especially when it comes to FICO and VantageScore ranges. Your score reflects how creditworthy you are. By regularly checking your score and taking steps to improve it, you can ensure that you’re in a better position.
What do the credit score ranges mean for you?
Lenders use your credit score range to determine whether you’re a trustworthy borrower. For matters of simplification, we’re using FICO scoring in this section.
Here’s what each FICO score tells creditors:
1. Poor Credit Score – (Under 580)
A Poor credit score indicates a severely damaged credit history. This number could be the result of multiple defaults or bankruptcy, which can stay in your record for ten years. Borrowers in this range are mostly unable to get new credit–and if they do, it’s often under risky terms.
2. Fair Credit Score – (580-669)
A Fair credit score still indicates poor credit behaviors, from late payments to a high amount of debt. Borrowers are often rejected for mainstream loans and may only be eligible for those with high-interest rates. Borrowers may also have to pay a fee or deposit or make larger down payments.
3. Good Credit Score – (670-739)
Once you enter this range, creditors see you as “acceptable.” Borrowers with Good scores have access to a broad range of loans and credit cards but will still pay higher interest rates than those with a Very Good or Excellent score.
4. Very Good Credit Score – (740-799)
People in this range qualify for even better rates and terms than those with a Good score.
5. Excellent Credit Score – (800 and up)
Lenders reward borrowers in this top range, offering the easiest approval process, lowest interest rates, and most favorable terms.
Why are there different credit score ranges?
As mentioned above, there isn’t one “credit score.” A variety of factors are responsible for this:
1. Reporting
Creditors report your activity to the credit bureaus. This includes credit card balances, payments made, amount of debt, and credit applications. Not all lenders send reports to the same credit bureaus–a late credit card payment may appear on just that bureau’s credit report.
2. Timing
Credit scores continuously change to reflect your credit use. While creditors report your activity every 45 days, they don’t share it at the same time. This can mean weekly or even daily changes to your credit score.
3. Scoring models
FICO and VantageScore provide the most common credit-scoring models. These companies pull info from the credit bureaus and use different algorithms and criteria to determine credit scores.
To complicate things, each company has multiple credit scoring formulas, also called “models.” Lenders can pull your base score or an industry-specific score, like for a mortgage or auto loan. Plus, there are different versions as models are updated (like software updates).
How do lenders use your credit score range?
Lenders use your credit score range to create borrower risk profiles which are as follows:
- Superprime: With a credit score of 720 and above, this profile indicates a financially responsible borrower. They are most likely to receive the best rates and terms.
- Prime: Borrowers with prime credit (660-719) can also still qualify for competitive rates and terms and are considered a lower risk. Rates may not be as low as superprime borrowers, but because their score indicates they are likely to repay their loans, they will likely still be approved for credit.
- Near Prime: With credit scores ranging from 620 to 659, whether you qualify for better borrowing terms and more competitive rates depends on where your score falls within the range. While these borrowers still can likely be approved for credit, their rates will be higher and terms less favorable. Keep in mind that borrowers with scores at the higher end of the range may be able to increase their score enough to get to Prime with on time payments and responsible credit management.
- Subprime: Experian data shows that 30% of consumers have a subprime credit score between 580 and 619. Typically, borrowers with this profile have more difficulty qualifying for loans and credit and if they are approved, rates and terms are much less favorable.
- Deep Subprime: If your score is below 580, you fall within the deep subprime category. These borrowers are considered the most risky to lenders, so they will have much greater difficulty finding a lender willing to approve a loan or credit card application. They will be offered lower limits and have a substantially higher interest rate. If you fall into this category, it’s best to improve your credit score before applying for a loan to improve your chances of approval.
It’s important to note that these are general borrower profiles, but each lender may have its own criteria for assessing risk and determining loan terms. Other factors such as income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio may also play a role in determining a borrower’s profile.
Why does having a good credit score matter?
There are several reasons you want to have as high of a credit score as possible. One of the biggest is that having a good credit score can help you qualify for loans with lower interest rates, which will help save you a lot of money over time. Other reasons include:
1. Get approved for borrowing and financing. Some lenders won’t approve loan or financing applications for borrowers who have poor credit, including credit card companies. This is because a poor score indicates your higher risk and may not repay the money you owe. On the other hand, a good credit score indicates you’ll repay what you owe within the loan term.
This is often the case for personal loans, credit cards, balance transfer credit cards, debt consolidation loans, and others. A good credit score shows you’re a trustworthy borrower.
2. Save money on car and homeowners insurance. Most states allow credit-based insurance scoring, so insurance companies can use your score to determine your risk based on how well you handle your money.
While other factors go into the underwriting process and they can’t penalize you for a bad score, having a good score may lower your premiums.
3. Renting an apartment is easier. A good credit score of at least 620 is typically the minimum credit score needed to qualify to rent an apartment. Some landlords are even more strict and require a score of 700 or above. The rental application process will be much easier and you’re more likely to qualify and be approved if your score is high.
4. Get access to better perks and rewards. The best credit cards with the best perks/rewards are typically only available to borrowers with good credit. This includes introductory offers, reward incentives, access to exclusive events or discounts, and more.
Learn more: Why a Good Credit Score Matters?
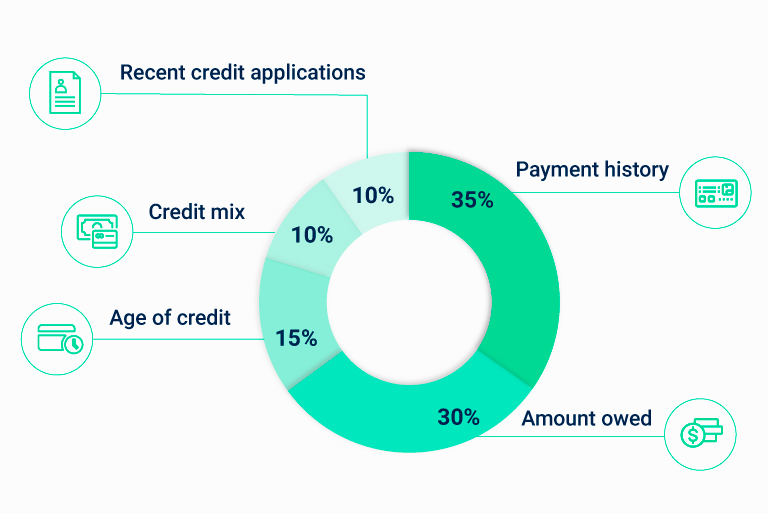
How’s my credit score calculated?
Lenders use a variety of credit scoring models to determine your risk. The most common model, FICO, weighs the following factors:
Source: Myfico.com
Learn more: How is Your Credit Score Calculated?
What is the highest credit score?
The highest credit score possible is 850; however, only about 1.3% of all FICO scores in the U.S. stand at 850. A perfect score is difficult, but not impossible to achieve. These consumers often have more credit products on their report and carry more credit cards than the national average, while also owing less.
Learn more: Highest Credit Score
What is the lowest score possible?
The lowest score possible is technically 300, though many financial institutions and lenders consider scores below 550 as the lowest and indicative of very poor financial history. Scores this low tend to mean the borrower has severely neglected their financial responsibilities, including late payments, collections, and bankruptcies.
Learn more: Lowest Possible Credit Score
What is the average credit score in the U.S.?
In 2022, the average FICO Score in the U.S. was 714. In past years, the score tended to increase:
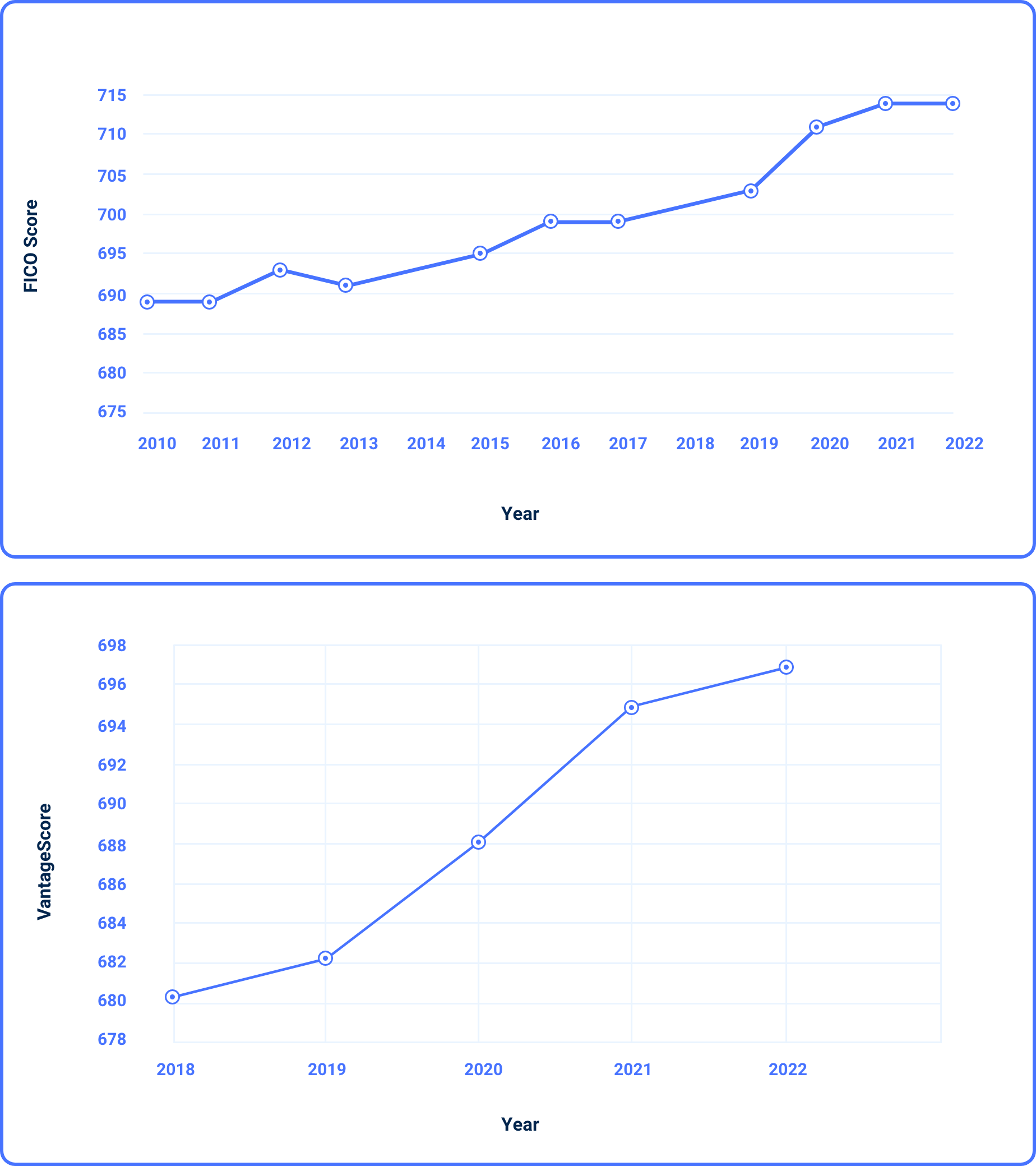
Even facing economic hardships over the past couple of years, including increasing interest rates and rising prices for goods and services, Americans are getting better about managing their finances and paying off debt.
Improve your credit score
No matter the model, boosting your credit score is always a good idea. Here are a few things you can do to increase your score:
- Check your credit report frequently. Your credit scores are all based on your credit report. Make sure to check your report for errors and dispute any inaccuracies.
- Always pay on time. Set up automatic payments whenever possible. Use calendar reminders to keep yourself on schedule.
- Don’t close out paid-off accounts: As long as there isn’t an annual fee,
Loan payoff calculatorCompare payoff methods by savings & more
Debt snowball calculatorEstimate your savings and debt-free date