What Is a FICO Score?
About Stefanie
Stefanie began her career as a journalist, reporting on options, futures, and pension funds, and most recently worked as a writer and SEO content strategist at a digital marketing agency. In her free time, she enjoys teaching Pilates and spending time with her daughter and Siberian Husky.
Read full bio
At a Glance
A FICO score is a credit score that gives lenders an idea of how likely you’ll be able to repay a loan. They use this score to make decisions about interest rates, the amount you can borrow, and your repayment period.
FICO is an abbreviation for the Fair Isaac Corporation, which developed the score in 1989. Your FICO score is three-digits and is based on a formula developed by FICO that takes numerous factors into consideration (more on that below):
Why FICO scores are important
Lenders use your FICO score to predict your future behavior and guide their loan decisions, like whether you should get a larger credit line. It gives banks a fast, streamlined way to assess whether you should get a loan, and under what terms.
A good FICO score will save you money, since it will most likely result in a bank giving you a lower interest rate than someone with bad credit. A low score could result in you being denied a loan or given a higher premium (ie., if you’re applying for a policy with an insurance company). In some situations, the bank will have a minimum score you must meet to qualify for a loan.
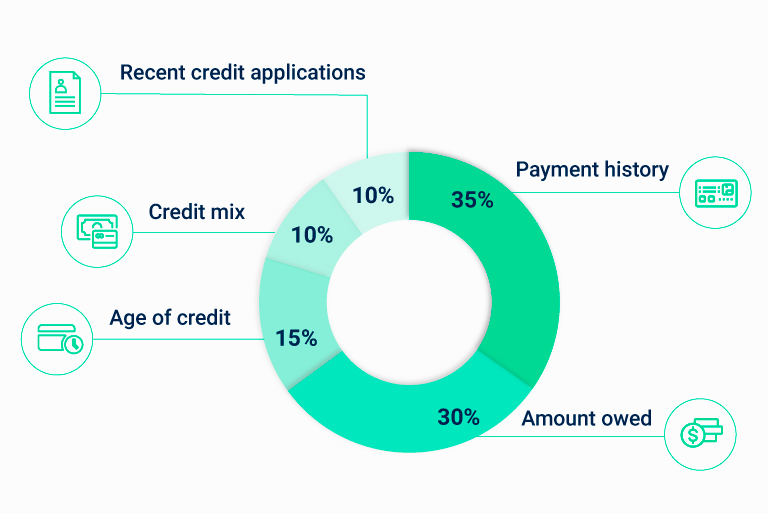
How FICO scores are calculated
Source: Myfico.com
What isn’t included in a FICO score
Your FICO score doesn’t take the following into account:
- Where you live
- Employment history
- Age
- Credit card interest rates
- Participation in credit counseling programs
- Religion, race, marital status, etc.
- Information not included in credit report
- Any information that isn’t proven to be an indicator of future credit performance
The FICO score range
FICO scores range from 300 to 850. The higher your FICO score, the better your credit.
What is considered a good score?
A FICO score of 670 and up is considered to be good. Anything below 579 is poor. Here is how the scores are broken down:
- 800 and up: Exceptional
- 740 to 799: Excellent
- 670 to 739: Good
- 580 to 669: Fair
- 579 or lower: Poor
How can you improve your score?
You can improve your FICO score by developing better credit habits. Examples include:
- Don’t borrow more than you need: Applying for a loan has a negative impact on your FICO score.
- Always pay on time: Since payment history is one of the biggest factors determining your FICO score, make sure to always pay on time. Setting up automatic payments is an easy way to keep yourself on schedule.
- Check your credit on a regular basis: You should take a look at your credit report at least once a year to see if something looks off, or if it’s time to change your habits.
- Maintain a low credit card balance: You can do this by making multiple payments each month or by limiting your credit card use.
Different types of FICO scores
There are dozens of FICO score models. They fall under two main categories: base scores and industry-specific scores. Industry-specific scores are used for specific credit products like auto loans. Lenders assess borrowers differently depending on the credit product, and each product has a different FICO model tailored to it. In addition, FICO has three different score versions that work with each of the biggest three credit bureaus: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
FICO has also made updates to its formulas over the years. FICO 8, which rolled out in 2009, is the most frequently used. FICO 9 is the newest update, but most mortgage lenders use older score versions.
Is a FICO score different from a credit score?
The terms “FICO score” and “credit score” are often used to mean the same thing, but a FICO score is just one type of credit score.
FICO vs. VantageScore
In 2006, the three major credit agencies created VantageScore, the second most popular credit score after FICO. VantageScore uses most of the same factors as FICO to determine your score. However, the biggest difference is that FICO covers credit histories of six months or longer, while VantageScore typically covers borrowers with a shorter credit history.
How to get a free FICO score
Some credit card companies offer access to a free monthly FICO score as a customer benefit. Call your credit card provider to see if a free score is part of their offerings.